Battery Type/'s
-Flooded Lead Acid,When the batteries are new, make
sure to charge the battery pack before its first use. Limit the use of new
batteries for first five cycles. New
batteries are not capable of their rated output until they have been discharged
a number of times. It takes 90-120 cycles
to fully maximize range.
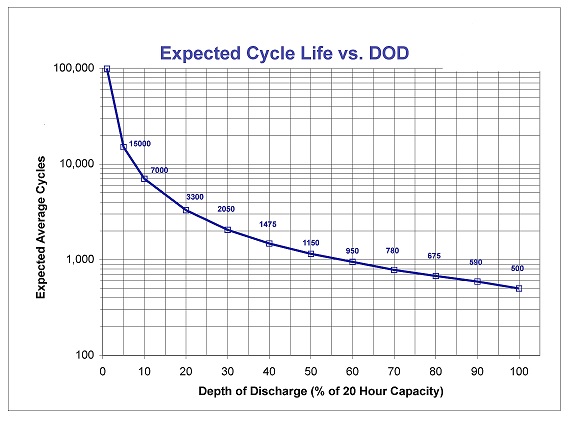
Do not excessively discharge batteries. Excessive discharge (below 63 volts) can cause polarity reversal of individual cells resulting in complete failure shortly thereafter. Routinely heavy discharging will also reduce the battery overall life as shown in Table 2 below. The battery depth of discharge as it relates to overall battery life is also shown in this table. Limited use of new batteries will also minimize the chance of cell reversal. Charge the batteries to their full state every two months whether you have used them or not to ensure they will not fully discharged.
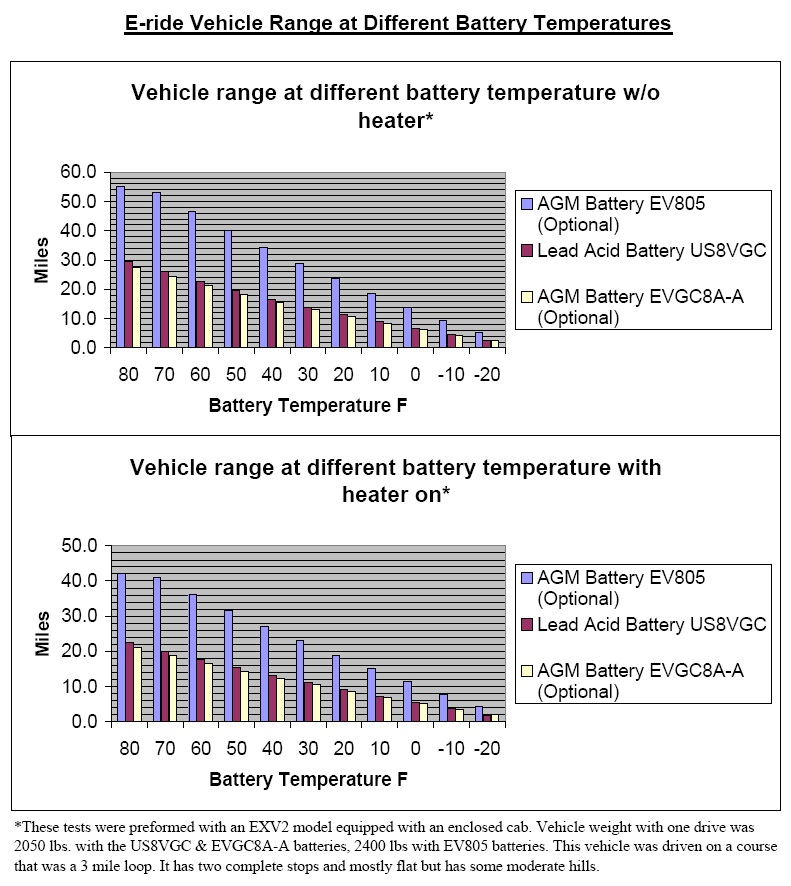
How temperature affects a batteries available capacity and charge
time
A batteries available capacity varies at various temperatures. As the ambient temperature rises a batteries ability to deliver current increases. As the temperature falls, so does the batteries ability to deliver current.
Cleaning and Maintenance
Make sure to fill batteries with
water monthly or promptly when there is any indicated need. The batteries must be refilled with distilled
or de-mineralized water to avoid internal damage. Electrolyte levels lower during discharge and
rise during charge. Therefore, it is mandatory that water be added to cells ONLY when they
are fully charged. Older batteries
may require more frequent watering than new batteries. (See section 2.2 for
battery watering procedure)
Keep the top of the batteries clean and dry to insure longer lasting, trouble-free operations. Also, make certain the battery cables are always tightly fastened to the battery terminals. Make sure the cables are tight to the terminals but be careful not to over tighten. Any corrosion present on the batteries or terminals should be cleaned promptly by brushing them off with a wire brush. The acid can be neutralized with a solution of baking soda and water.
Lead Acid
If the vehicle will be stored for any period of time, check battery electrolyte level, adjust level if needed and then connect battery charger to vehicle. Allow charger to re-main connected to vehicle during storage to prevent battery discharge and potential battery damage. If the vehicle will be stored for more than 30 days and the battery charger cannot be used for some reason, charge the batteries fully. Either store batteries on a shelf or in the vehicle. Store the batteries in a cool atmosphere to avoid quick deterioration of the charge in the batteries. To prevent batteries from freezing, make sure they are fully charged before storage. During the storage period, charge the batteries at least once every three (3) months to prevent battery damage. Before returning the vehicle to service, make sure to fully charge the batteries. Batteries ending there life can discharge faster.
Do not park the vehicle and leave it for any length of time with discharged batteries. The batteries could discharge to the point where damage could occur and the battery charger will not charge. If you allow the vehicle to sit in conditions of 32°F (0°C) or less with a state of charge of 20% or less, the batteries could freeze. If the batteries happen to freeze, it may cause damage to the batteries and permanently reduce their capacity. The battery case could also crack if it is frozen. Inspect for this before attempting to thaw. Place the vehicle in an area greater than 32°F and allow it to warm up before charging. Never charge the vehicle if the batteries may be frozen.
When storing batteries during off-season or any time while the vehicle is not in use for any length of time, follow these guide lines to help keep the batteries in good condition.
1. Keep
the batteries clean and free of corrosion as outlined in section 3.5.3.
2. Fully
charge the batteries prior to storage.
3. Store
in a cool area. The colder temperature
in which the batteries are stored, the less they will self discharge. Batteries stored at 0°F will discharge very little over a four month period. Batteries stored at 80°F will have to be recharged every few weeks.
4. The
frequency of recharging required will depend on the temperature of the storage area, but it is
recommended that the batteries be monitored for state of charge every month. Also, if the storage area is unheated in a
cold climate recharge is required. It is
recommended that the area be heated to at least 60°F prior to charge.
Batteries do not charge effectively in cold temperatures for the same
reason that they do not discharge as rapidly in cold temperatures.
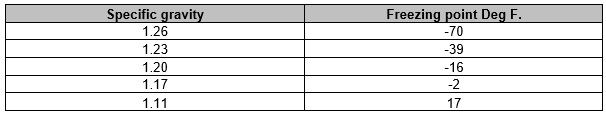
5. Check the state of charge periodically. Batteries that are discharged and left in the cold environment can freeze and crack. If the specific gravity drops below 1.220, the batteries should be recharged. See Table 2 below.
The following table shows the freezing point of a battery based on the specific gravity of the acid. This gives a guideline for working temperatures at a certain specific gravity.